Explorations and Applications of Enzyme-linked Bioremediation of Synthetic Dyes
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 27 May 2024

Extensive use of synthetic dyes and their subsequent release in industrial wastewater is a growing environmental problem. These dyes are recalcitrant in nature, and some dyes are also well established to be potentially carcinogenic and mutagenic as well as genotoxic. Research efforts have been devoted to develop new, low-cost, and eco-friendly treatments capable of reducing and even eliminating synthetic dye compounds from the environment. Enzymatic approach has attracted much interest recently in the decolorization of textile and other industrially important dyes from wastewater as an alternative strategy to conventional chemical, physical, and biological treatments, which pose serious limitations. In this chapter, the accumulated research data on the potential of the oxidoreductive enzymes—high redox potential peroxidases (lignin peroxidase [LiP], EC 1.11.1.14; manganese peroxidase [MnP], EC 1.11.1.13; dye decolorizing peroxidase [DyP], EC 1.11.1.19; and versatile peroxidases [VP], EC 1.11.1.16), laccases (benzenediol–oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.10.3.2), polyphenol oxidases (EC 1.14.18.1), and azoreductases (azobenzene reductases, EC 1.7.1.6)—that have been exploited in the decolorization and degradation of synthetic dyes are presented. An overview of enzyme technology, including the importance of redox mediators for enhanced range of substrates and efficiency of degradation, current biodegradation applications, and suggestions to overcome the limitations to these proteins’ large scale and efficient use, is made. Different strategies currently being used and future prospects for the potential use of genetic engineering techniques to improve the performance of these oxidoreductases in terms of stability, selectivity, and catalytic activity in dye bioremediation technologies are also explored.
Frontiers The potential of fungi in the bioremediation of pharmaceutically active compounds: a comprehensive review

Decoding dye degradation: Microbial remediation of textile industry effluents - ScienceDirect

PDF) Biodegradation of textile dyes waste water by Pleurotus eryngii

Full article: Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches for evaluation of laccase-mediated biodegradation of various industrial dyes
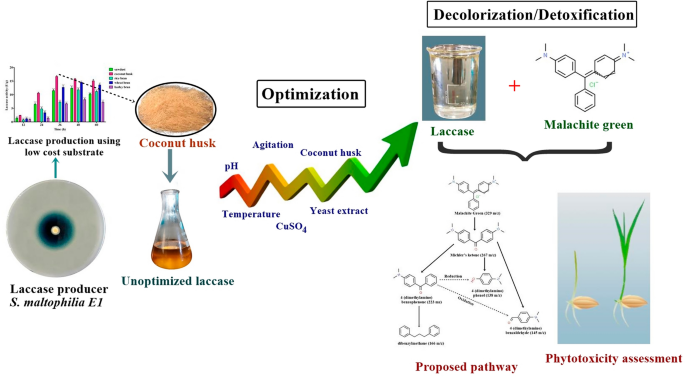
Optimization of laccase from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia E1 by submerge fermentation using coconut husk with its detoxification and biodecolorization ability of synthetic dyes, Bioresources and Bioprocessing

PDF) Studies on the Biodegradation of Azo Dyes by White Rot Fungi Phlebia Radiata

In Silico Analysis of Bacterial Systems For Textile Azo Dye Decolorization and Affirmation With Wetlab Studies - Srinivasan - 2017 - CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water - Wiley Online Library
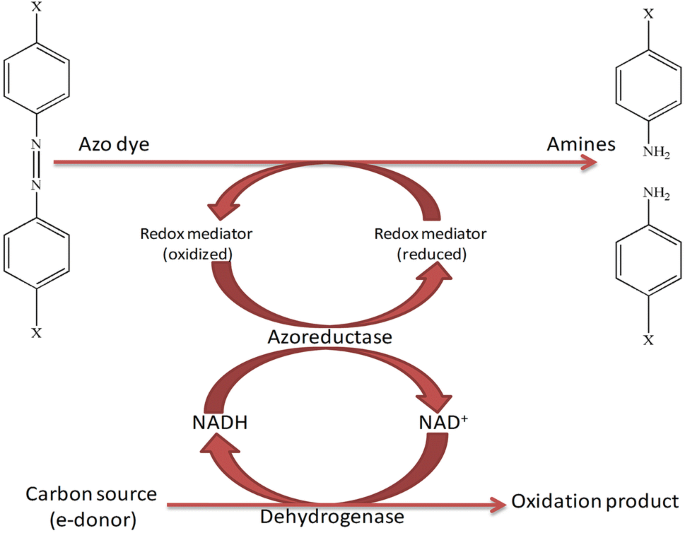
Applicability of enzymes produced from different biotic species for biodegradation of textile dyes

PDF) Explorations and Applications of Enzyme-linked Bioremediation of Synthetic Dyes

Bioremediation of wastewater containing azo dyes through sequential anaerobic–aerobic bioreactor system and its biodiversity
Recommended for you
-
 Rit DyeMore, Art, Rit Dyemore Synthetic Dye27 May 2024
Rit DyeMore, Art, Rit Dyemore Synthetic Dye27 May 2024 -
 We need to talk about the synthetic dyes in our clothes27 May 2024
We need to talk about the synthetic dyes in our clothes27 May 2024 -
 Chemical and Synthetic Dyes27 May 2024
Chemical and Synthetic Dyes27 May 2024 -
 Natural dyes v synthetic: which is more sustainable?, Guardian sustainable business27 May 2024
Natural dyes v synthetic: which is more sustainable?, Guardian sustainable business27 May 2024 -
 Knowledge for Collections: Early synthetic dyes27 May 2024
Knowledge for Collections: Early synthetic dyes27 May 2024 -
 Rit Dyemore Synthetic Liquid27 May 2024
Rit Dyemore Synthetic Liquid27 May 2024 -
 A Brief Introduction to Synthetic Dyes - imgroupofresearchers27 May 2024
A Brief Introduction to Synthetic Dyes - imgroupofresearchers27 May 2024 -
 Do or dye: Synthetic colors in wastewater pose a threat to food chains worldwide27 May 2024
Do or dye: Synthetic colors in wastewater pose a threat to food chains worldwide27 May 2024 -
 Engineering this fungi may produce eco-friendly alternative to27 May 2024
Engineering this fungi may produce eco-friendly alternative to27 May 2024 -
 Mauve Mania - Science Museum Blog27 May 2024
Mauve Mania - Science Museum Blog27 May 2024
You may also like
-
 Plier Organizers (Lisle 40490 & MLTools P8248)27 May 2024
Plier Organizers (Lisle 40490 & MLTools P8248)27 May 2024 -
 Barnwood Picture Frames 24x30 Frame Whitewash Lighthouse27 May 2024
Barnwood Picture Frames 24x30 Frame Whitewash Lighthouse27 May 2024 -
 1000d Cordura27 May 2024
1000d Cordura27 May 2024 -
 Indoor Camping Stove, Airless and Electric Camping Stove, Camping Stove with Pot27 May 2024
Indoor Camping Stove, Airless and Electric Camping Stove, Camping Stove with Pot27 May 2024 -
 Wholesale 3m rubbing compound For Super Long-Lasting Paint Protection27 May 2024
Wholesale 3m rubbing compound For Super Long-Lasting Paint Protection27 May 2024 -
 Goof Off Pro Strength Remover - 6 oz27 May 2024
Goof Off Pro Strength Remover - 6 oz27 May 2024 -
 55 Heart Silicone Molds with Dropper27 May 2024
55 Heart Silicone Molds with Dropper27 May 2024 -
 Stainless Steel Wax Carver Tools Dental Waxing Instruments with Case,pottery tool kit polymer clay Carver Set for Sculpting, Detailing, Pottery27 May 2024
Stainless Steel Wax Carver Tools Dental Waxing Instruments with Case,pottery tool kit polymer clay Carver Set for Sculpting, Detailing, Pottery27 May 2024 -
 Create This Book 2 (Moriah Elizabeth) - Episode 327 May 2024
Create This Book 2 (Moriah Elizabeth) - Episode 327 May 2024 -
 What Can't Go in a U-Box® Container? - Moving Help®27 May 2024
What Can't Go in a U-Box® Container? - Moving Help®27 May 2024