MRI contrast agents: Classification and application (Review)
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 18 Jun 2024
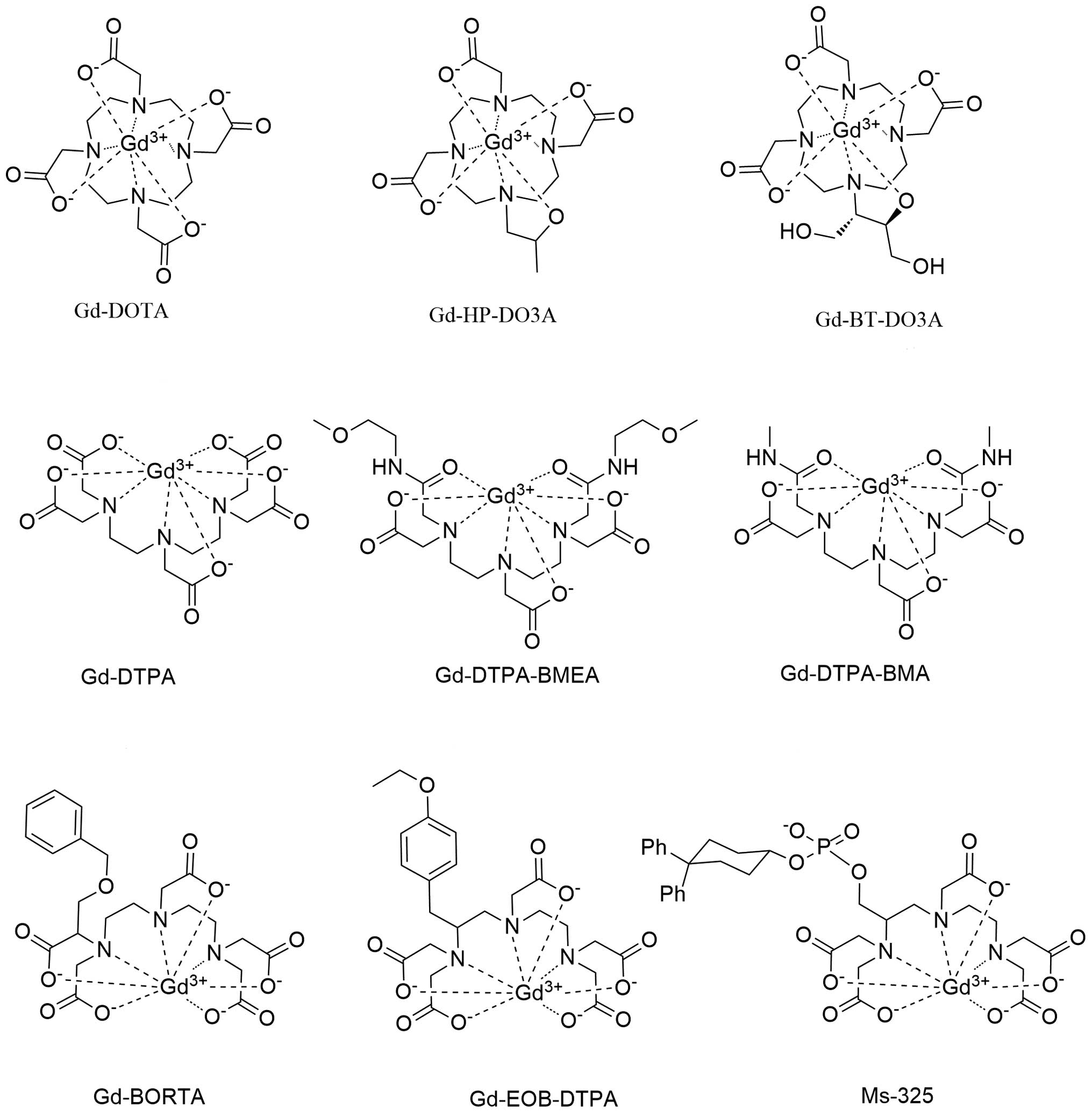
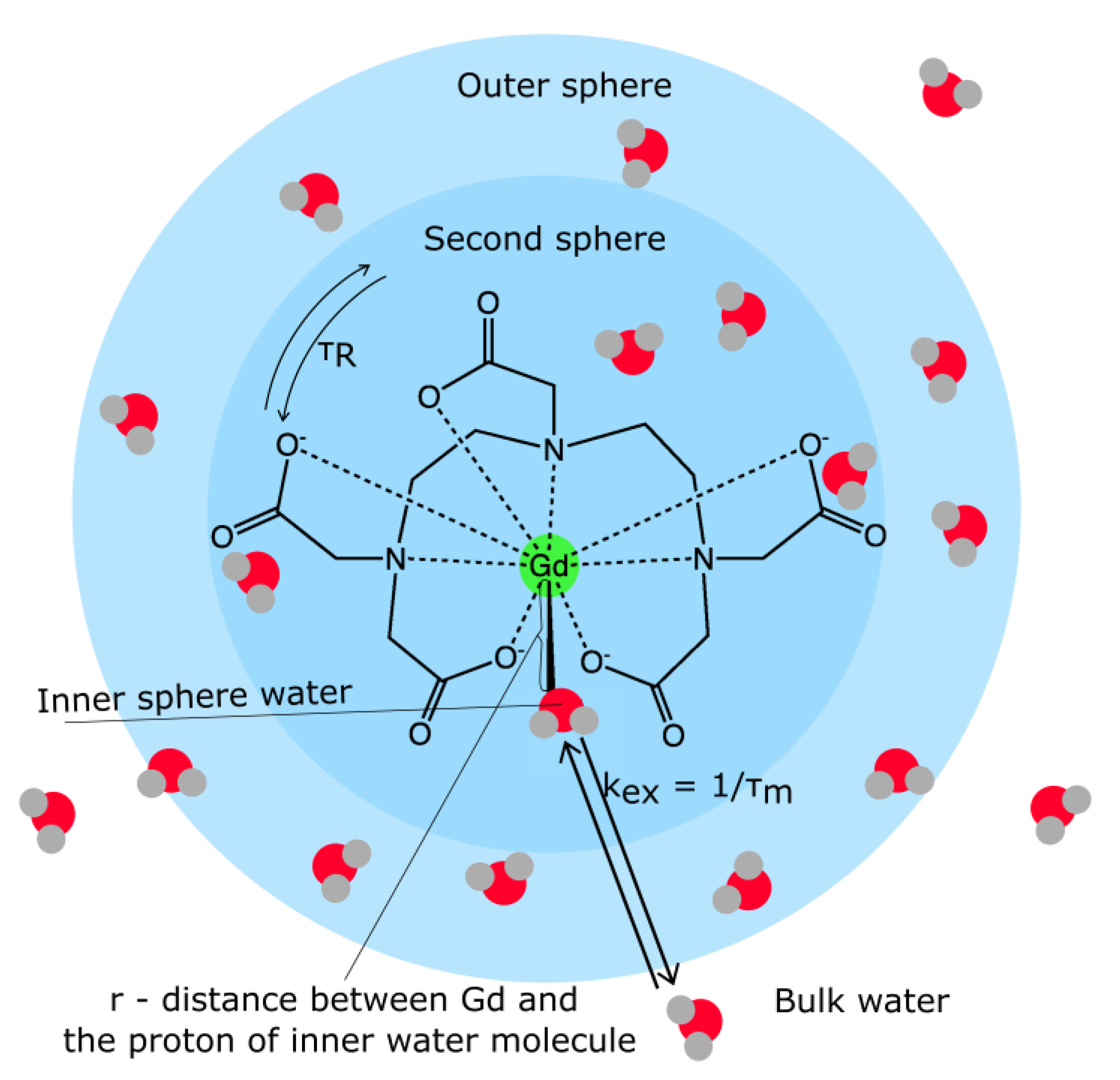
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents are categorised according to the following specific features: chemical composition including the presence or absence of metal atoms, route of administration, magnetic properties, effect on the magnetic resonance image, biodistribution and imaging applications. The majority of these agents are either paramagnetic ion complexes or superparamagnetic magnetite particles and contain lanthanide elements such as gadolinium (Gd3+) or transition metal manganese (Mn2+). These elements shorten the T1 or T2 relaxation time, thereby causing increased signal intensity on T1-weighted images or reduced signal intensity on T2-weighted images. Most paramagnetic contrast agents are positive agents. These agents shorten the T1, so the enhanced parts appear bright on T1-weighted images. Dysprosium, superparamagnetic agents and ferromagnetic agents are negative contrast agents. The enhanced parts appear darker on T2-weighted images. MRI contrast agents incorporating chelating agents reduces storage in the human body, enhances excretion and reduces toxicity. MRI contrast agents may be administered orally or intravenously. According to biodistribution and applications, MRI contrast agents may be categorised into three types: extracellular fluid, blood pool and target/organ-specific agents. A number of contrast agents have been developed to selectively distinguish liver pathologies. Some agents are also capable of targeting other organs, inflammation as well as specific tumors.

Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New

PDF) MRI contrast media: What clinicians need to know

Materials, Free Full-Text
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text
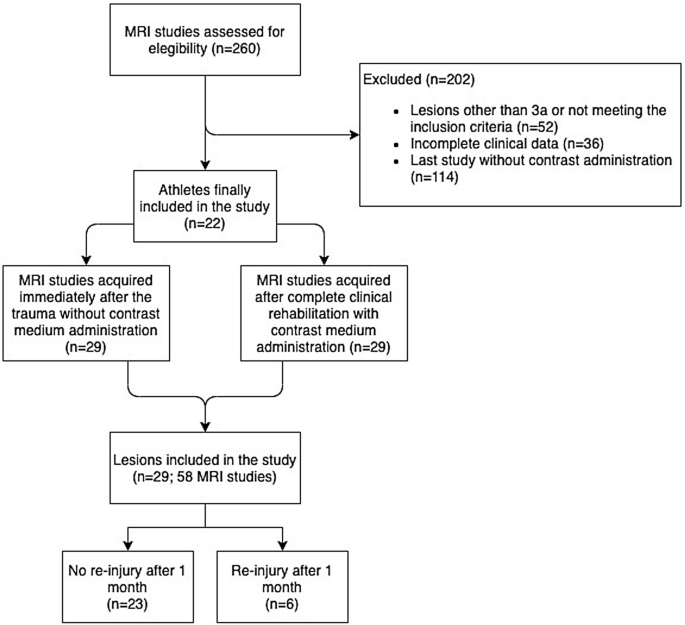
Paramagnetic contrast medium in high-level athletes with lower limb muscle injuries: can it make the return to sport safer reducing the recurrence rate?

The effect of gadolinium-based contrast agent administration on magnetic resonance fingerprinting-based T1 relaxometry in patients with prostate cancer
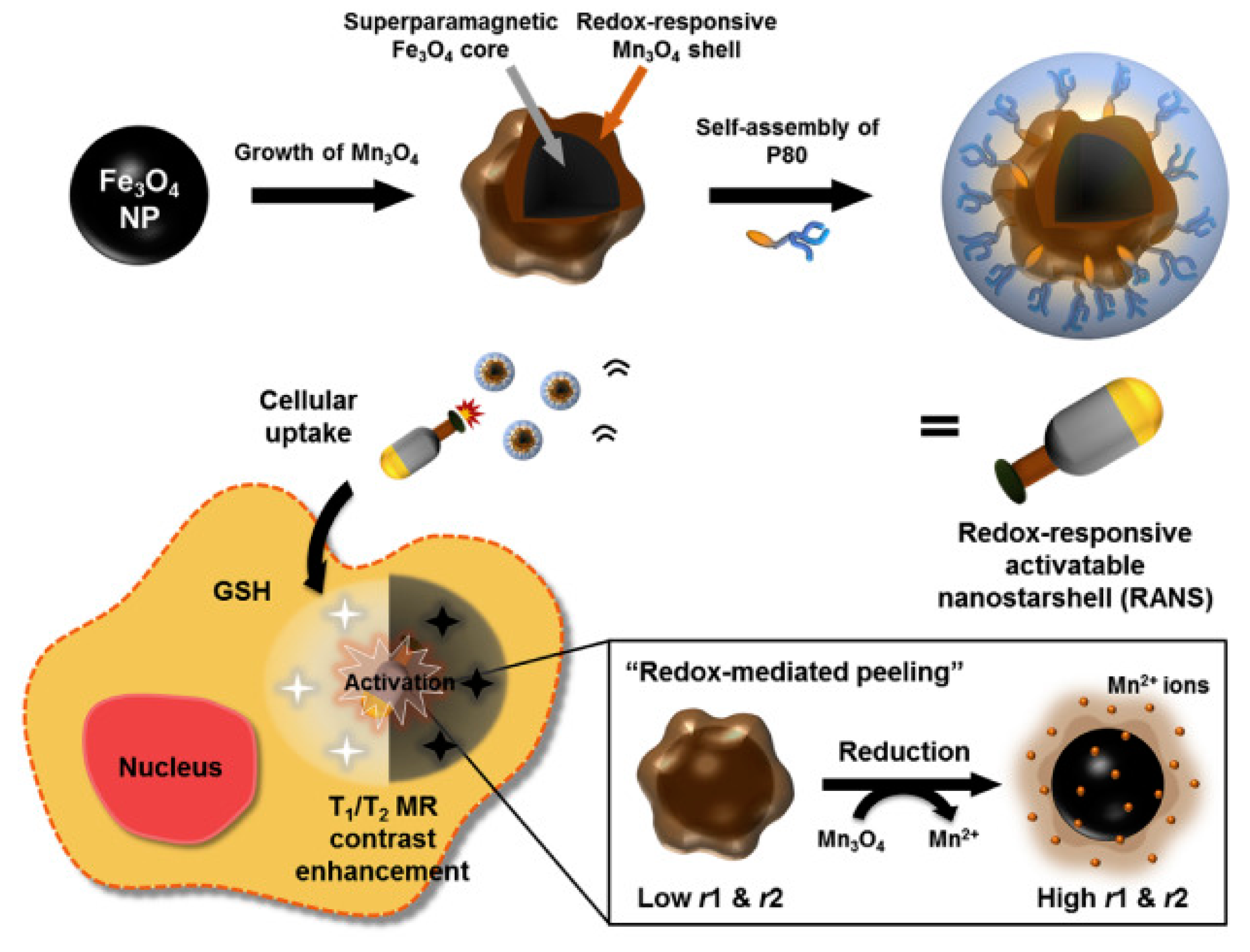
Pharmaceuticals, Free Full-Text

Cell sorting microbeads as novel contrast agent for magnetic
Recommended for you
-
 Contrast medium, MRI, CT scan & X-ray18 Jun 2024
Contrast medium, MRI, CT scan & X-ray18 Jun 2024 -
 Contrast Media - Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital18 Jun 2024
Contrast Media - Radiology at St. Vincent's University Hospital18 Jun 2024 -
 Technical: Contrast Medium (24ml)18 Jun 2024
Technical: Contrast Medium (24ml)18 Jun 2024 -
 Contrast Media Genetek Lifesciences18 Jun 2024
Contrast Media Genetek Lifesciences18 Jun 2024 -
 Extravasation of Iodinated Contrast Medium During CT: Self-Assessment Module18 Jun 2024
Extravasation of Iodinated Contrast Medium During CT: Self-Assessment Module18 Jun 2024 -
Nontraumatic intravasation of myelographic contrast medium18 Jun 2024
-
 Figure2, Intraventricular Contrast Medium Leakage during Ethanol Embolization of an Arteriovenous Malformation18 Jun 2024
Figure2, Intraventricular Contrast Medium Leakage during Ethanol Embolization of an Arteriovenous Malformation18 Jun 2024 -
 Xray Opaque Contrast Medium That Shows Stock Photo 32558767118 Jun 2024
Xray Opaque Contrast Medium That Shows Stock Photo 32558767118 Jun 2024 -
 Explanation of terms. The contrast medium aortic arrival time is18 Jun 2024
Explanation of terms. The contrast medium aortic arrival time is18 Jun 2024 -
 200ml Single Use High-Pressure Contrast Medium Injector Syringes18 Jun 2024
200ml Single Use High-Pressure Contrast Medium Injector Syringes18 Jun 2024
You may also like
-
 Cynthia Urban on X: Math + Art = Pythagorean Spiral Project at GHSNice Job Sebastian! / X18 Jun 2024
Cynthia Urban on X: Math + Art = Pythagorean Spiral Project at GHSNice Job Sebastian! / X18 Jun 2024 -
 Taylor Swift Eras Lineup | Poster18 Jun 2024
Taylor Swift Eras Lineup | Poster18 Jun 2024 -
 7 Sealing color Tape Rolls 2 x 110 Yards Packaging BLUE - Light weight18 Jun 2024
7 Sealing color Tape Rolls 2 x 110 Yards Packaging BLUE - Light weight18 Jun 2024 -
 Dritz 45 Degree Angle Quilting Ruler-4X1218 Jun 2024
Dritz 45 Degree Angle Quilting Ruler-4X1218 Jun 2024 -
 Boost CX1 Parquet18 Jun 2024
Boost CX1 Parquet18 Jun 2024 -
 Bug Bite Thing is Antidote for Mosquitos, and Now Ticks18 Jun 2024
Bug Bite Thing is Antidote for Mosquitos, and Now Ticks18 Jun 2024 -
 Portable Wiper Rear View Mirror - Temu18 Jun 2024
Portable Wiper Rear View Mirror - Temu18 Jun 2024 -
 Koala Tools 2-point Perspective 3D Grid Sketchbook 10.75x8.2 - The Paint Spot - Art Supplies and Art Classes, Edmonton18 Jun 2024
Koala Tools 2-point Perspective 3D Grid Sketchbook 10.75x8.2 - The Paint Spot - Art Supplies and Art Classes, Edmonton18 Jun 2024 -
 White Wood Easel – Affordable & Luxury Event Rentals18 Jun 2024
White Wood Easel – Affordable & Luxury Event Rentals18 Jun 2024 -
 Flat Glass Marbles Decor Vase, Marbles Decoration Vases18 Jun 2024
Flat Glass Marbles Decor Vase, Marbles Decoration Vases18 Jun 2024