KapMA Kit - Methacrylated Kappa-Carrageenan Kit - Adbioink
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 26 May 2024
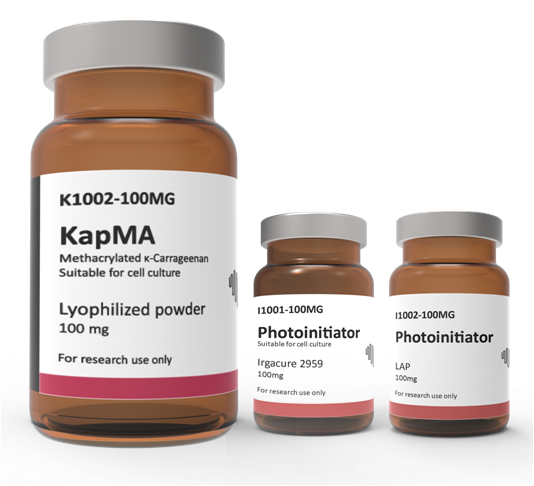
Carrageenan is a hydrophilic polymer extracted from algae and is used as a gelling agent and emulsifying agent. Among different types of carrageenan, Kappa-carrageenan (κCA), a natural linear water-soluble polysaccharide with one sulphated group per disaccharide (25 to 30% ester sulfate content), is one of the appropriate biomaterial in tissue engineering. κCa has been seen as a potential candidate for this area in injectable form, due to its gelation properties, mechanical strength and resemblance to chondroitin-4-sulfate anddermatan sulfate, which are the major components of native extracellular matrices (ECM) called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). κCar is a thixotropic polymer and can be converted into hydrogel form via ionic crosslinking method. However, these crosslinking methods offer hydrogels that have low stability in physiologic conditions. In order to overcome this drawback, κCA is methacrylating to synthesis KapMA with photopolymerization potential. κ-CA has a characteristic of tunable viscosity depending on concentration, temperature, the presence of ions and molecular weight and has properties of high strength, nontoxic and cellular compatibility. As its shear-thinning and thermo-reversible properties are suitable for bioinks, κ-CA could been chosen as a bioink material for 3D extrusion-based bioprinting.

K131H Stemco Kaiser Qwik Kit No Ream King Pin Set Hendrickson Tag Axle

Microwave assisted methacrylation of Kappa carrageenan: A bioink for cartilage tissue engineering - ScienceDirect
Product Overview The STAKIT is a Terminal Kit with metal carrying case. Eliminates missed crimps increases conductivity and insulator stays on barrel.

Thomas & Betts STAKIT Kit, Terminal/Splice
Cape Crystal Kappa Carrageenan is a food-grade organic natural thickener, stabilizer & gelling agent. It is a vegan and kosher alternative to bovine gelatin, and used in molecular gastronomy, modernist cooking. A staple in molecular gastronomy and modernist cooking, kappa carrageenan powder is often used in flans, puddings, chocolate, and other flavored milk and soy-based beverages, and, as a source of dietary fiber.

Cape Crystal Kappa Carrageenan Powder Food Grade Natural Thickener substitute for Gelatin - Kosher ( 8 oz)
Carrageenan is a hydrophilic polymer extracted from algae and is used as a gelling agent and emulsifying agent. Among different types of carrageenan,
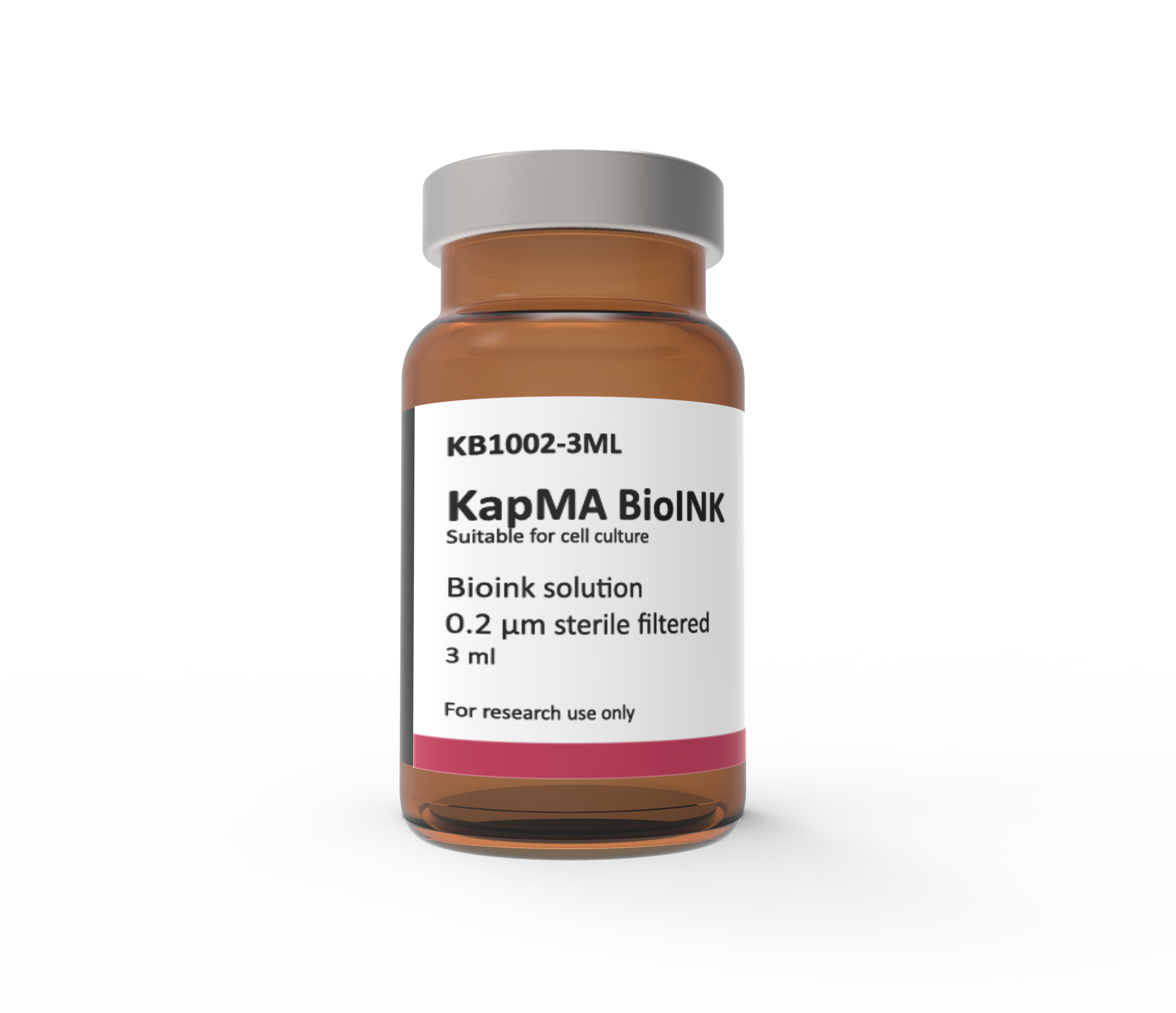
KapMA Kit - Methacrylated Kappa-Carrageenan Kit

Microwave assisted methacrylation of Kappa carrageenan: A bioink for cartilage tissue engineering - ScienceDirect
Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting technologies are a tool used to obtain functional human tissues and organs used for regenerative medicine or drug
BioPen-X (Handheld Bioprinter)
Carrageenan is a hydrophilic polymer extracted from algae and is used as a gelling agent and emulsifying agent. Among different types of carrageenan,

KapMA Kit - Methacrylated Kappa-Carrageenan Kit
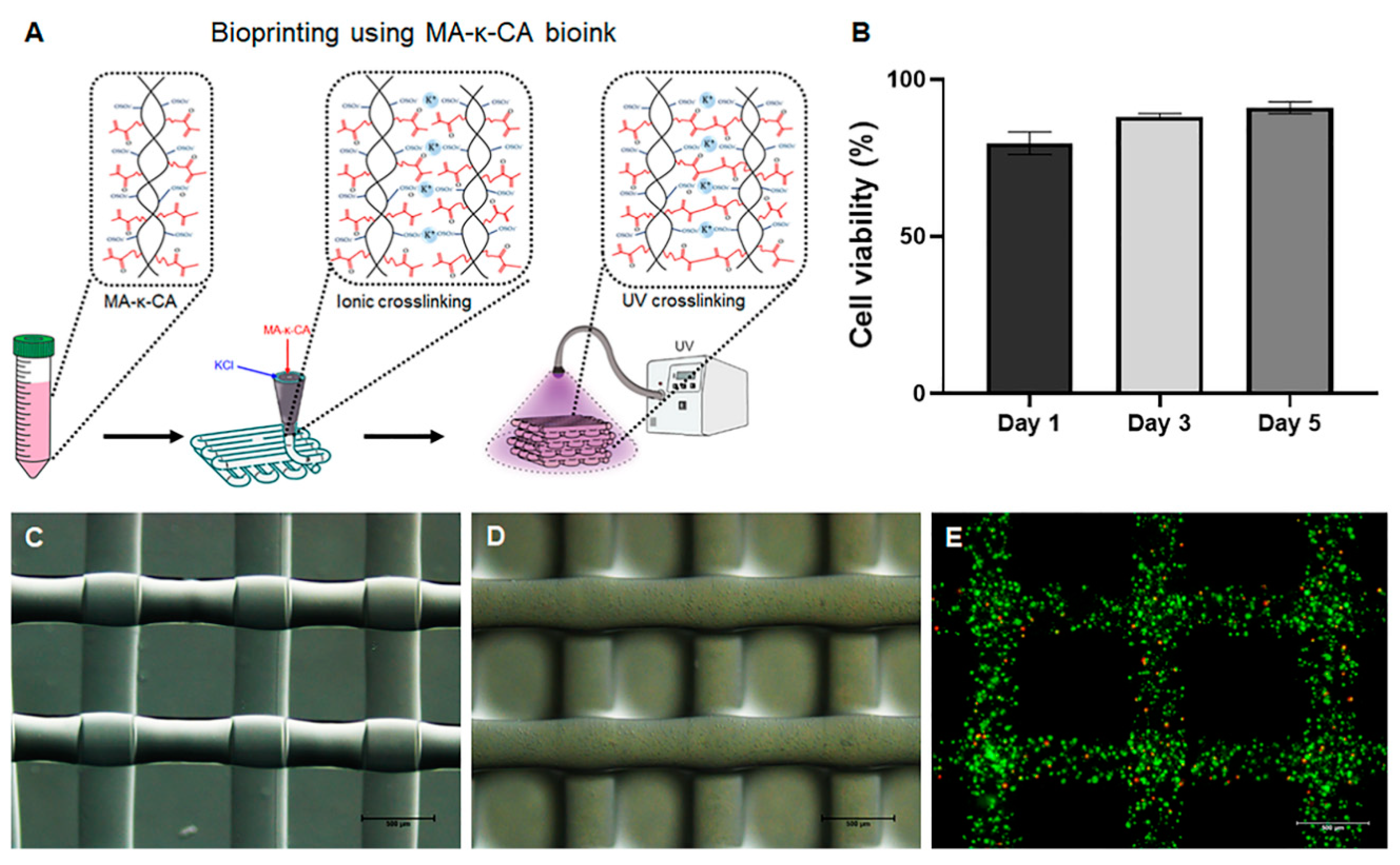
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Methacrylate κ-carrageenan (KaMA) synthesis and hydrogel formation.

Microwave assisted methacrylation of Kappa carrageenan: A bioink for cartilage tissue engineering - ScienceDirect

Microwave assisted methacrylation of Kappa carrageenan: A bioink for cartilage tissue engineering - ScienceDirect
Recommended for you
-
![Kappa Carrageenan 100G / 3.5Oz [Made For Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/7153mCS++LL.jpg) Kappa Carrageenan 100G / 3.5Oz [Made For Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]26 May 2024
Kappa Carrageenan 100G / 3.5Oz [Made For Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]26 May 2024 -
 Wholesale Food Additive Food Grade Kappa Carrageenan Powder - China Carrageenan, CAS 9000-07-126 May 2024
Wholesale Food Additive Food Grade Kappa Carrageenan Powder - China Carrageenan, CAS 9000-07-126 May 2024 -
![Urban Platter Kappa Carrageenan 100g / 3.5oz [Made for Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]](https://i5.walmartimages.com/asr/7056d8fe-1880-4ac8-b744-2e0e3183bb97.17a0d8f49592206f213c11f713c2ecfa.jpeg?odnHeight=768&odnWidth=768&odnBg=FFFFFF&format=avif) Urban Platter Kappa Carrageenan 100g / 3.5oz [Made for Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]26 May 2024
Urban Platter Kappa Carrageenan 100g / 3.5oz [Made for Milk-Based Water-Based Applications]26 May 2024 -
 Carrageenan (Blender Type)26 May 2024
Carrageenan (Blender Type)26 May 2024 -
 Kappa Carrageenan - Modernist Pantry, LLC26 May 2024
Kappa Carrageenan - Modernist Pantry, LLC26 May 2024 -
 Half Pound Lambda Carrageenan Powder Supplies for Marbling on26 May 2024
Half Pound Lambda Carrageenan Powder Supplies for Marbling on26 May 2024 -
 5lbs Bulk Carrageenan Powder for Water Marbling With Acrylic Paint26 May 2024
5lbs Bulk Carrageenan Powder for Water Marbling With Acrylic Paint26 May 2024 -
 Food and Industrial Grade 100% Natural Lambda Carrageenan Powder26 May 2024
Food and Industrial Grade 100% Natural Lambda Carrageenan Powder26 May 2024 -
 China Food Additives Carrageenan Powder K Jelly Suppliers26 May 2024
China Food Additives Carrageenan Powder K Jelly Suppliers26 May 2024 -
 China Customized Magical Ingredient From Nature: Discover26 May 2024
China Customized Magical Ingredient From Nature: Discover26 May 2024
You may also like
-
 Wig Comb Clips Wigs, Wig Cap Comb Clips26 May 2024
Wig Comb Clips Wigs, Wig Cap Comb Clips26 May 2024 -
 Kopter Precision Thin Point Tweezers26 May 2024
Kopter Precision Thin Point Tweezers26 May 2024 -
 Lovely Rainbow and Daisy Candles, Rainbow Candles, Daisy Candles, Rainbow Birthday Decorations, Rainbow Birthday Candles, Daisy Decor26 May 2024
Lovely Rainbow and Daisy Candles, Rainbow Candles, Daisy Candles, Rainbow Birthday Decorations, Rainbow Birthday Candles, Daisy Decor26 May 2024 -
 Round Floating Wicks - 50 Count (Approx.), Large Cotton Wicks and Cork Disc Holders for Oil Cups - Bonus Wick Removal Tweezers - by Ner Mitzvah26 May 2024
Round Floating Wicks - 50 Count (Approx.), Large Cotton Wicks and Cork Disc Holders for Oil Cups - Bonus Wick Removal Tweezers - by Ner Mitzvah26 May 2024 -
 Wreath Of Small Red, Pink And Purple Christmas Tree Balls On Window Handle Greeting Card by Friedrich Strauss26 May 2024
Wreath Of Small Red, Pink And Purple Christmas Tree Balls On Window Handle Greeting Card by Friedrich Strauss26 May 2024 -
 Freediver Shop 1kg / 2.2 lbs Lead Belt Weight26 May 2024
Freediver Shop 1kg / 2.2 lbs Lead Belt Weight26 May 2024 -
-700x700.jpeg) Selleys Ready Mix Wallpaper Adhesive Glue 1 Litre For Wallpaper Glue26 May 2024
Selleys Ready Mix Wallpaper Adhesive Glue 1 Litre For Wallpaper Glue26 May 2024 -
 Personalized Photo Books Make Special Gifts - A Cowboy's Wife26 May 2024
Personalized Photo Books Make Special Gifts - A Cowboy's Wife26 May 2024 -
 Silicone Painting Mat Silicone Art Mat With Water Cup For - Temu26 May 2024
Silicone Painting Mat Silicone Art Mat With Water Cup For - Temu26 May 2024