Facilitated Event-Related Power Modulations during Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Revealed by Concurrent tACS-MEG
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 17 Jun 2024

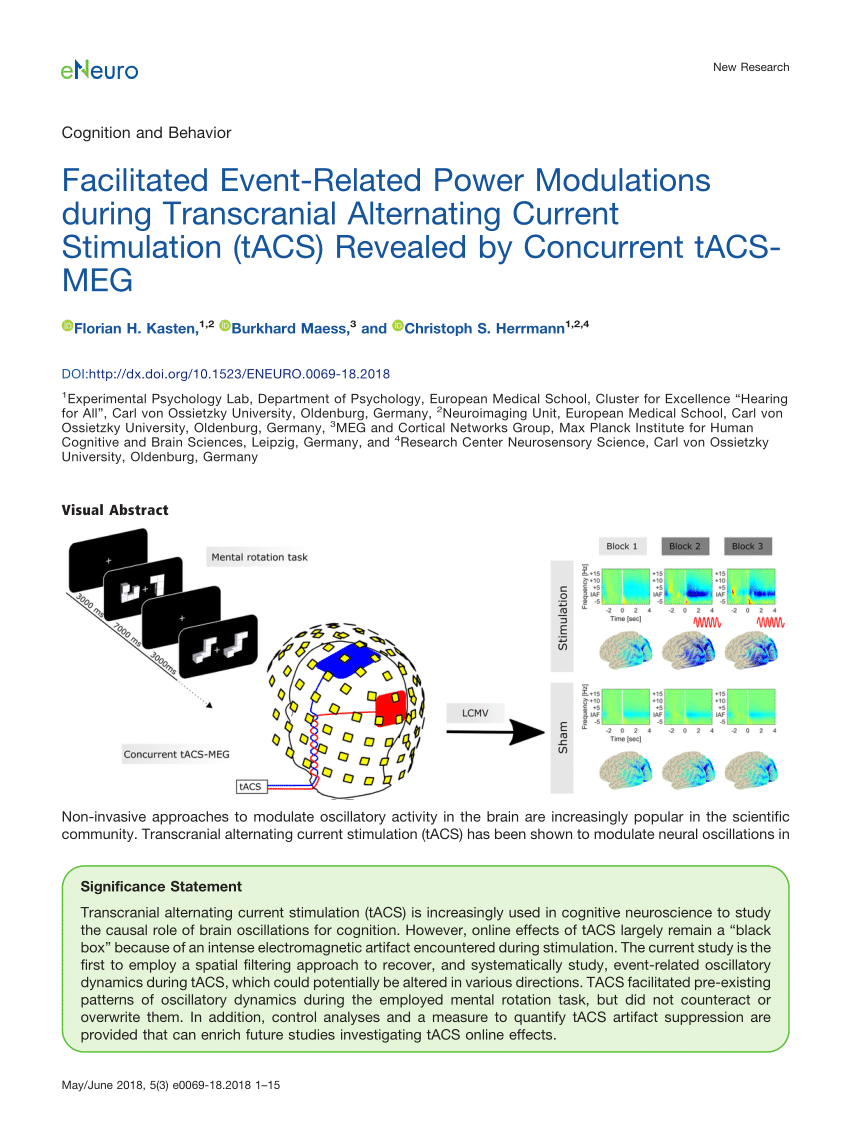
Non-invasive approaches to modulate oscillatory activity in the brain are increasingly popular in the scientific community. Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) has been shown to modulate neural oscillations in a frequency-specific manner. However, due to a massive stimulation artifact at the targeted frequency, little is known about effects of tACS during stimulation. It remains unclear how the continuous application of tACS affects event-related oscillations during cognitive tasks. Depending on whether tACS influences pre- or post-stimulus oscillations, or both, the endogenous, event-related oscillatory dynamics could be pushed in various directions or not at all. A better understanding of these effects is crucial to plan, predict, and understand outcomes of solely behavioral tACS experiments. In the present study, a recently proposed procedure to suppress tACS artifacts by projecting MEG data into source-space using spatial filtering was utilized to recover event-related power modulations in the alpha-band during a mental rotation task. MEG data of 25 human subjects was continuously recorded. After 10-minute baseline measurement, participants received either 20 minutes of tACS at their individual alpha frequency or sham stimulation. Another 40 minutes of MEG data were acquired thereafter. Data were projected into source-space and carefully examined for residual artifacts. Results revealed strong facilitation of event-related power modulations in the alpha-band during tACS application. These results provide first direct evidence that tACS does not counteract top-down suppression of intrinsic oscillations, but rather enhances pre-existent power modulations within the range of the individual alpha (= stimulation) frequency.

Probing the Link Between Perception and Oscillations: Lessons from Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation - Yuranny Cabral-Calderin, Melanie Wilke, 2020

Vision modulation, plasticity and restoration using non-invasive brain stimulation – An IFCN-sponsored review - ScienceDirect

The hidden state-dependency of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)
PDF) Facilitated Event-Related Power-Modulations during Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Revealed by Concurrent tACS-MEG

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Attenuates Visual Motion Adaptation
Integrating electric field modeling and neuroimaging to explain inter-individual variability of tACS effects

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation - an overview
Online and offline effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation of the primary motor cortex
Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text

Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation Attenuates Visual Motion Adaptation
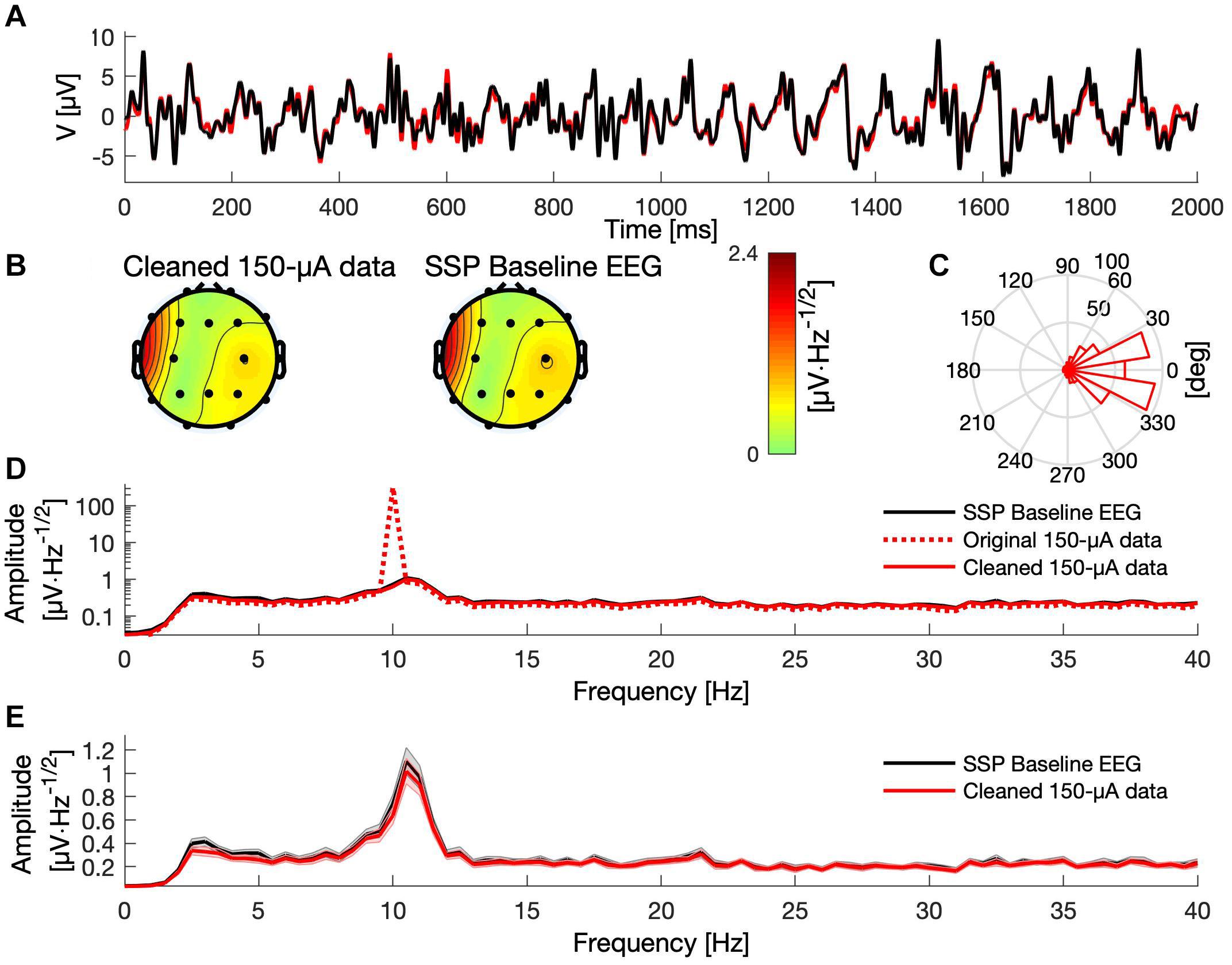
Frontiers Signal-Space Projection Suppresses the tACS Artifact
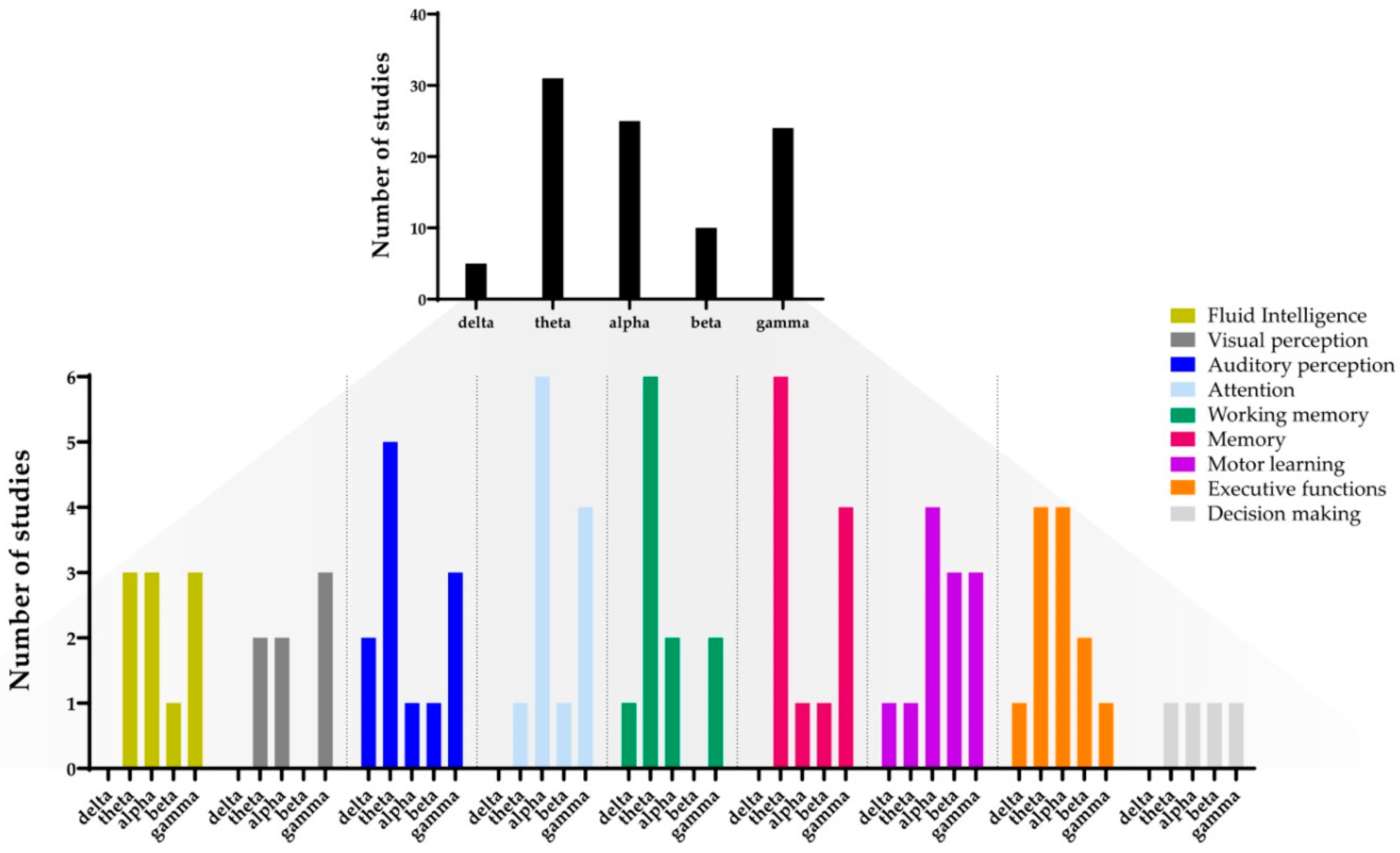
Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text

Brain Sciences, Free Full-Text
Recommended for you
-
Tic Tac Fruit Adventure Mint Candies - 1oz17 Jun 2024
-
 Texas Association of Community Schools - About Us17 Jun 2024
Texas Association of Community Schools - About Us17 Jun 2024 -
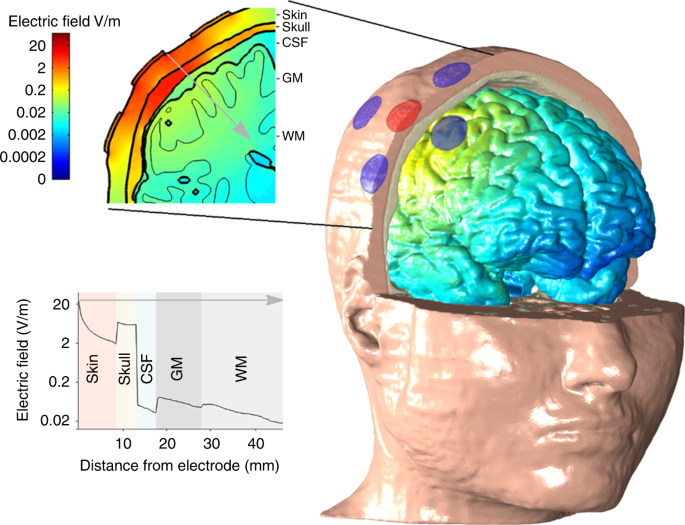 tACS motor system effects can be caused by transcutaneous stimulation of peripheral nerves17 Jun 2024
tACS motor system effects can be caused by transcutaneous stimulation of peripheral nerves17 Jun 2024 -
EEG and tACS electrode montages and tACS current simulation results. A17 Jun 2024
-
 A-TACs Camo - Print On-Demand Fabric17 Jun 2024
A-TACs Camo - Print On-Demand Fabric17 Jun 2024 -
 Buy A-Tacs Printed Kydex, Officially Licensed Patterns17 Jun 2024
Buy A-Tacs Printed Kydex, Officially Licensed Patterns17 Jun 2024 -
 TACS Automatic Vintage Lens Watch17 Jun 2024
TACS Automatic Vintage Lens Watch17 Jun 2024 -
 1.1 oz Silpoly, A-TACs AU Camo17 Jun 2024
1.1 oz Silpoly, A-TACs AU Camo17 Jun 2024 -
 Current flow during tACS. When current is applied sinusoidally, the17 Jun 2024
Current flow during tACS. When current is applied sinusoidally, the17 Jun 2024 -
 Time and Attendance Collection System - TACS17 Jun 2024
Time and Attendance Collection System - TACS17 Jun 2024
You may also like
-
 Delicious Tangerine Neon Dip Dye Taper Candles — Lost Objects, Found Treasures17 Jun 2024
Delicious Tangerine Neon Dip Dye Taper Candles — Lost Objects, Found Treasures17 Jun 2024 -
 Superior Products California Cover All Automotive Tire Shine Aerosol Spray Can17 Jun 2024
Superior Products California Cover All Automotive Tire Shine Aerosol Spray Can17 Jun 2024 -
 Mad Hatter Tea Party Themed Birthday Party – FREE Printable's - The Supermoms Club17 Jun 2024
Mad Hatter Tea Party Themed Birthday Party – FREE Printable's - The Supermoms Club17 Jun 2024 -
 Double Sided PA Hot Melt Adhesive Film Glue Sheet For Embroidery Patch Textile Fabric17 Jun 2024
Double Sided PA Hot Melt Adhesive Film Glue Sheet For Embroidery Patch Textile Fabric17 Jun 2024 -
 Mod Podge Dishwasher Safe, Gloss Finish, 32 fl oz, Clear17 Jun 2024
Mod Podge Dishwasher Safe, Gloss Finish, 32 fl oz, Clear17 Jun 2024 -
 Leather bracelet making kit, Sami bracelet supplies, Gift for crafty woman, Sewing kit for beginners, Cute craft kit for girl, Sewers gift17 Jun 2024
Leather bracelet making kit, Sami bracelet supplies, Gift for crafty woman, Sewing kit for beginners, Cute craft kit for girl, Sewers gift17 Jun 2024 -
 DIGITAL KEY GREEN TAPE 50 YARD ROLL17 Jun 2024
DIGITAL KEY GREEN TAPE 50 YARD ROLL17 Jun 2024 -
 Naomi Home Everly Wall-Mounted Whiteboard - Naomi Home17 Jun 2024
Naomi Home Everly Wall-Mounted Whiteboard - Naomi Home17 Jun 2024 -
 Cartoon Princesses Adult Coloring Pages - Israel17 Jun 2024
Cartoon Princesses Adult Coloring Pages - Israel17 Jun 2024 -
 1000pcs -safety Pins, Safety Pins Bulk Metal Silver Sewing Pins17 Jun 2024
1000pcs -safety Pins, Safety Pins Bulk Metal Silver Sewing Pins17 Jun 2024
